Kaspersky Global Research & Analysis Team (GReAT) discovered hundreds of open source repositories with multistaged malware targeting gamers and cryptoinvestors within a new campaign that was dubbed by Kaspersky as GitVenom. The infected projects include an automation instrument for interacting with Instagram accounts, a Telegram bot that enables the remote management of Bitcoin wallets and a crack tool to play the Valorant game. All of this alleged project functionality was fake, and cybercriminals behind the campaign stole personal and banking data and hijacked cryptowallet addresses from the clipboard. As a result of the malicious activity cybercriminals were able to steal 5 Bitcoins (around $485,000 at the time of investigation). Kaspersky detected the use of the infected repositories worldwide, with most cases in Brazil, Turkiye, and Russia.
These repositories
have been stored on GitHub, a platform that allows developers to manage and
share their code, for several years. The attackers strived to make the
repositories on GitHub appear legitimate to potential targets by using
attractive project descriptions that have likely been generated with AI. If the
code from these repositories was launched, the victim’s device would become
infected with malware and could be remotely controlled by the attackers.
While the projects were written in multiple programming languages – Python, JavaScript, C, C++ and C# – the malicious payloads stored inside the infected projects had the same goal: to download other malicious components from an attacker-controlled GitHub repository and execute them. These components include a stealer that collects passwords, bank account information, saved credentials, cryptocurrency wallet data and browsing history, packs it into a .7z archive and uploads it to attackers via Telegram.
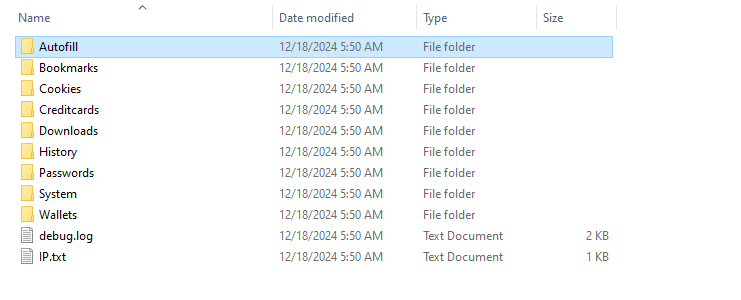
Structure of the archive which the stealer
sends to attackers
Other downloaded
malicious components include remote administration tools that can be used to
remotely monitor and control a victim’s computer through a secure encrypted
connection, and a clipboard hijacker which searches the clipboard contents for
cryptocurrency wallet addresses and replaces them with attacker-controlled
ones. Notably, the attacker-controlled Bitcoin wallet received a sum of about 5
BTC (approximately $485,000 at the time of research) in November 2024.
“As code sharing platforms such as GitHub are used by millions of
developers worldwide, threat actors will certainly continue using fake software
as an infection lure in the future. For that reason, it is crucial to handle
processing of third-party code very carefully. Before attempting to run such
code or integrate it into an existing project, it is paramount to thoroughly
check what actions are performed by it. This way, it will be very easy to spot
fake projects and prevent malicious code placed in them from being used to
compromise the development environment,” comments Georgy Kucherin,
Security Researcher at Kaspersky GReAT.
Read more on Securelist.com.
About the Global Research &
Analysis Team
Established in 2008,
Global Research & Analysis Team (GReAT) operates at the very heart of
Kaspersky, uncovering APTs, cyber-espionage campaigns, major malware,
ransomware and underground cyber-criminal trends across the world. Today GReAT
consists of 35+ experts working globally – in Europe, Russia, Latin America,
Asia and the Middle East. Talented security professionals provide company
leadership in anti-malware research and innovation, bringing unrivaled
expertise, passion and curiosity to the discovery and analysis of cyberthreats.




