It would be hard to find a sphere of human activity untouched by the coronavirus pandemic, and express delivery services are no exception. Transport flows between countries have been disrupted, and there is a shortage of cargo planes as people and companies continue to order goods both domestically and from abroad. Demand for some items has even shot up.
The spikes in demand are causing in-transit times to stretch out. As a result, customers are getting used to receiving apologetic messages from couriers linking to updated shipping status. Recently, we have observed a number of fake sites and e-mails supposedly from delivery services exploiting the coronavirus topic. Fraudsters are using both tried-and-true ploys and new schemes.
Spam with malicious attachments
Spammers may pose as delivery service employees to persuade victims to open malicious e-mail attachments. The classic trick is to say that to receive a package that’s come in, the recipient must first read or confirm the information in an attached file.
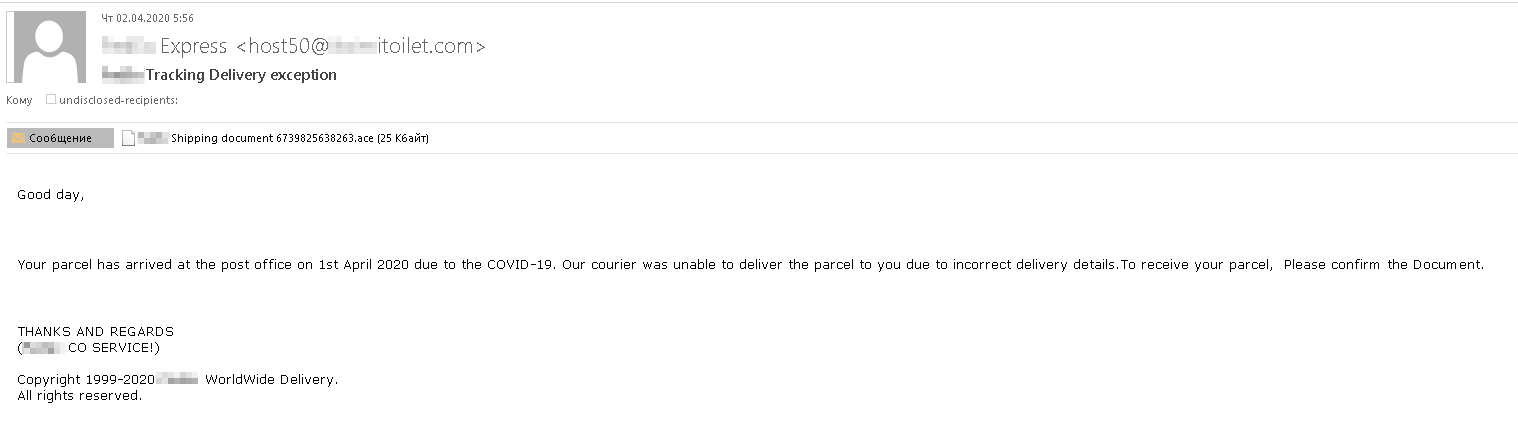
For example, a fake delivery notification e-mail in broken English says that a parcel cannot be delivered because of the pandemic, so the recipient needs to come to the warehouse and pick it up in person.
The warehouse address and other details are, of course, said to be in the attachment — which, if opened, installs a Remcos backdoor on the computer. Cybercriminals can then make the PC join a botnet, or they might steal data or install other malware.
The authors of another fake delivery e-mail use a similar trick, alleging that the company was unable to deliver the package because of a labeling error. The victim is asked to confirm the information in the attachment, which in fact contains another member of the Remcos family.
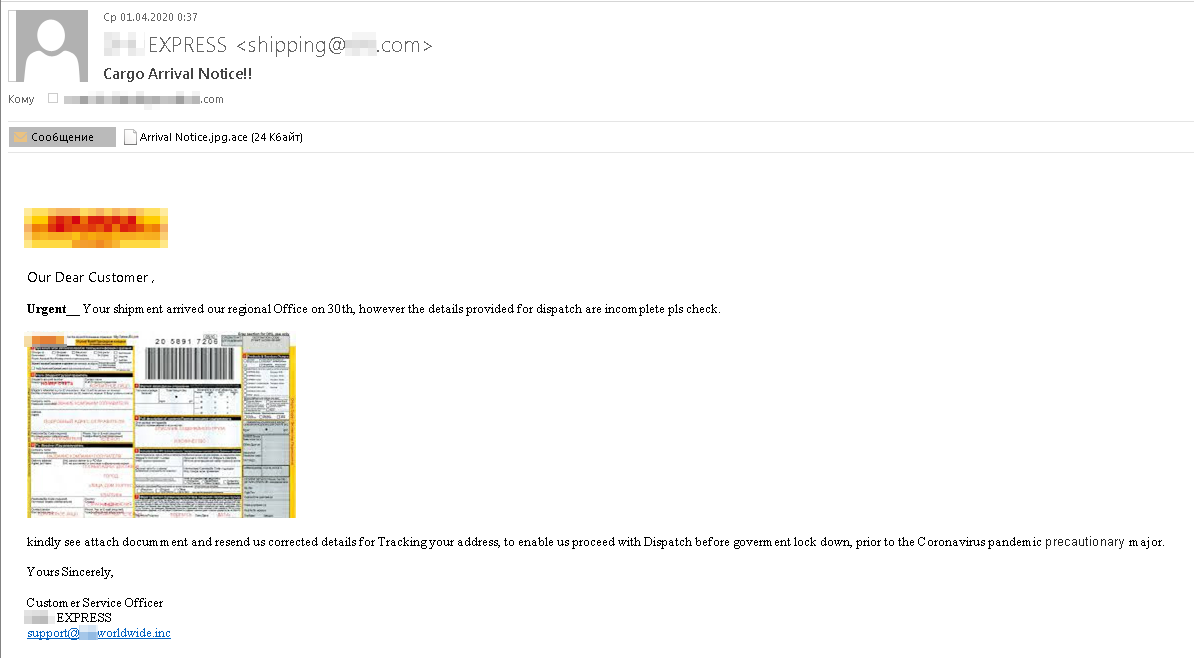
These crooks are pretending to be from a certain express delivery company, but the address gives them away
Sometimes spammers insert images of documents in a message to add credibility. In the example below, scammers added a small image to the e-mail text. It appeared to be a receipt, but it was too small to read and did not change size when clicked, prompting the recipient to open the malicious attachment, whose name contains “.jpg.”
If the recipient’s e-mail client does not display the file’s real extension, they might mistake such an attachment for the image. It’s actually an executable ACE archive containing the spyware program Noon.
To rush the victim, the cybercriminals say they need the missing information urgently so as to deliver the parcel before lockdown.
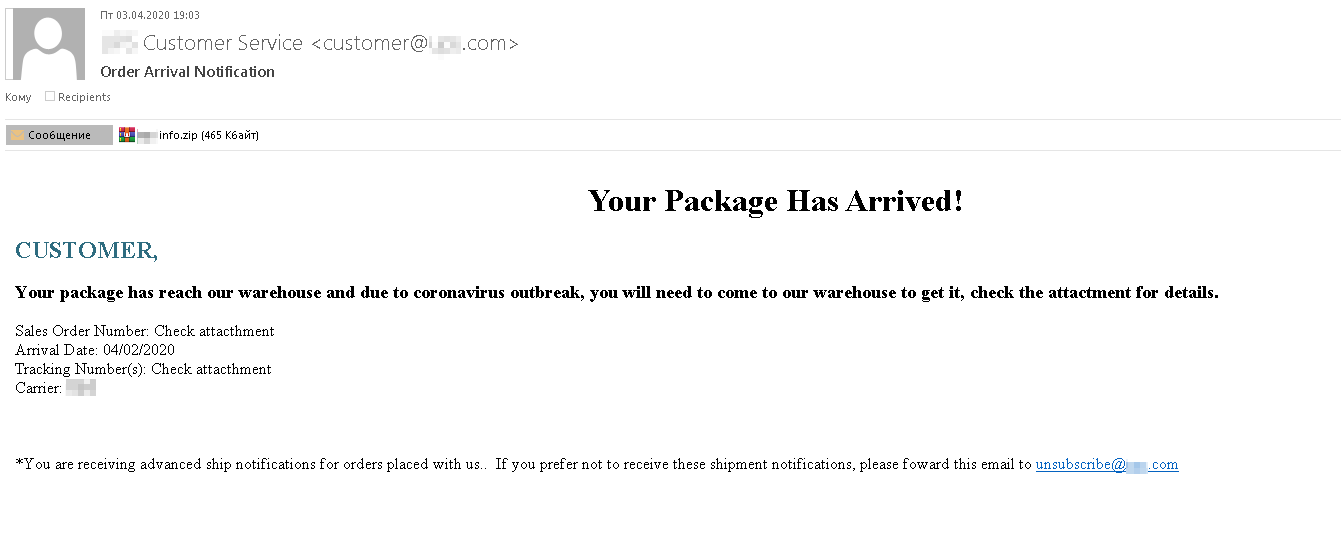
Another malicious e-mail topic that’s not new but is especially relevant in the current climate is delivery delays. The scenario is highly plausible: The scammers point the victim to an attachment that contains the Bsymem Trojan, which if executed enables the attackers to take control of the device and steal data. The bottom of the message includes a statement that it was scanned by a mail security solution and found to contain no malicious files or links, a claim designed to lull the recipient into a false sense of security.
Many spammers simply insert a mention of COVID-19 into their usual mailing templates, but some focus specifically on quarantines and the rapid spread of the pandemic.
For example, in one story, the government had banned the import of any kind of goods into the country, so the package was returned to the sender.
The attachment supposedly contains an order tracking number to request a reshipment after virus-related health restrictions subside. Opening the file, however, risks installing the Androm backdoor, which gives the attackers remote access to the computer.
Phishing
Scammers specializing in phishing attacks are also taking advantage of delivery market chaos. We detected highly believable copies of legitimate websites as well as fake tracking pages. All of them, of course, made mention of the coronavirus.
For example, phishers targeting accounts of a delivery service customers replicated the company’s official homepage in detail, including the latest news about the pandemic.
No less detailed is this clone of another delivery service website, which also mentions the latest coronavirus news.
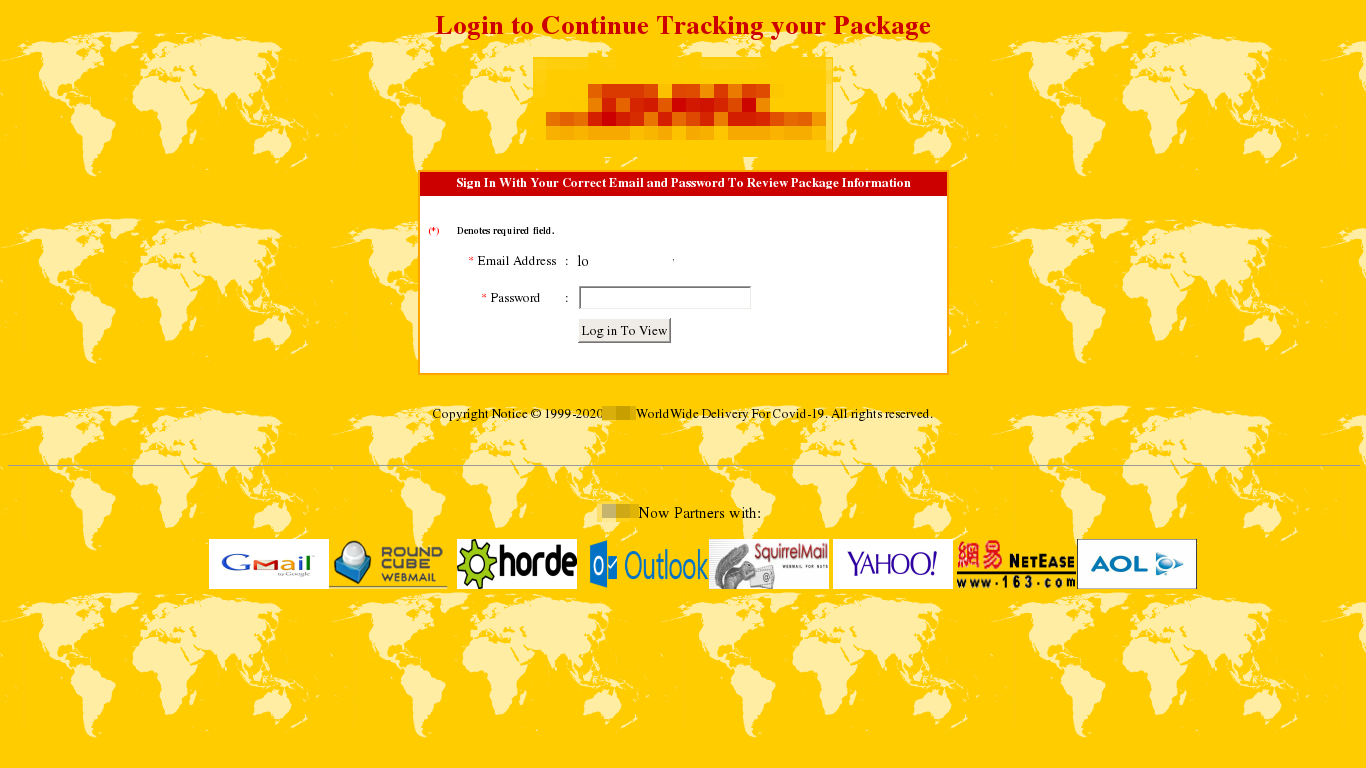
The authors of this fake portal for tracking packages added COVID-19 to the copyright line. There is little other information on the page: a form for entering credentials and a list of “partner” e-mail services. Needless to say, entering credentials on this resource sends them to the scammers, and the fate of the package will remain unknown.
How not to swallow the bait
Against the backdrop of the pandemic and the large number of genuine package delays, fake sites and e-mails have a good chance of success — especially if you really are expecting a package, or if, say, shipment details were sent to your work e-mail and you have reason to think that a colleague might have placed the order. To avoid getting hooked:
- Look carefully at the sender’s address. If the message came from a free e-mail service or contains a meaningless set of characters in the mailbox name, it’s most likely a fake. Keep in mind though, that it’s possible to forge sender address.
- Pay attention to the text. A major company will never send e-mails with crookedly formatted text and bad grammar.
- Do not open attachments in e-mails from delivery services, especially if the sender insists on it. Instead, log in to your personal account on the courier’s website, or manually enter the address of the service in your browser to check the tracking number. Do likewise if you received an e-mail urging you to click a link.
- Take special care if a message makes any mention of coronavirus. Cybercriminals exploit hot topics to attract attention, so you should never rush to comply with such messages.
- Install a reliable security solution that detects malicious attachments and blocks phishing websites.
 spam
spam





 Tips
Tips